Home / Resources / Glucerna / Guide Your Day

Guide Your Day
Tips for Diabetes Management
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood.
It happens when there is not enough insulin, or the body does not use it effectively. Insulin opens the body’s cells to allow sugar to enter and provide energy.
If you lack insulin, or if your body does not use it properly, sugar accumulates in the blood.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes generally occurs during childhood or adolescence, because the pancreas does not produce insulin.
Treatment
With type 1 diabetes, insulin is needed to manage properly your blood sugar levels. For that, most likely need to take insulin shots or wear an insulin pump. It can also be managed between nutrition and physical activity.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is commonly diagnosed in adulthood, and it is because the body may not produce enough insulin and/or does not work effectively in the body. It is possible that some young people can also present this type of diabetes.
TreatmentType 2 diabetes can be managed maintaining a balance between nutrition, physical activity and in some cases, the use of medications.
Diabetes & Its Care
Stay Physically Active
Start exercising for 10 or 15 minutes until you can reach 30 or 60 minutes.
Eat Nutritious & Balanced Meals
Eating a healthy diet, focusing on balancing carbohydrate foods throughout the day as well as low in saturated fat and salt helps maintain a healthy balance and promote overall health.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
People who are tested more often have a better management of their blood glucose.
Visit The Doctor
Schedule two to four monitoring visits, in addition to annual doctor visit and routine eye exams.
Take Your Medications
Take medications as directed by your doctor.
Do Not Smoke
Smoking increases the likelihood of several complications of diabetes.
If you drink Alcohol, do so responsibly
Alcohol can raise or lower blood glucose, depending on how much you drink and whether you eat at the same time. If you decide to drink do it in moderation, that is, no more than one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men.
Check Your Feet!
A high blood glucose level can reduce the blood flow and damage the nerves in the feet.
Take Stress Seriously
If you’re stressed, it’s easy to neglect your usual diabetes care routine. Control your stress by setting limits, prioritizing tasks and learning relaxation techniques.
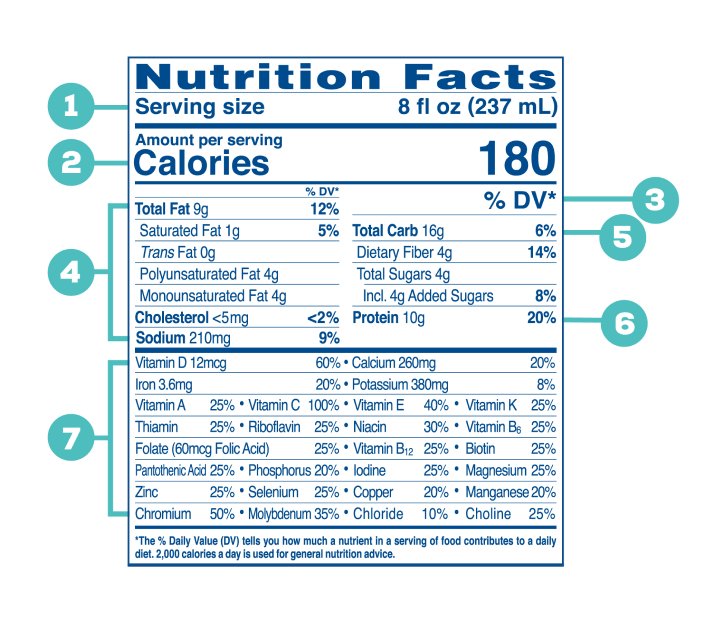
1. Serving size
Shows how many servings are in the package/product and what size each serving is. All label information is based on one serving of the food.
2. Amount of calories
Calories listed are for one serving of the food.
• 40 calories: Low
• 100 calories: Moderate
• 400 calories or more: High
3. DV% Daily Value
Indicates how the nutrients in one serving contribute to a diet based on 2,000 calories. Choose foods that are high in nutrients that you should
eat more (20% DV) and low in nutrients that you should eat less (5% DV).
4. Limit these nutrients
Eating too much fat (specially saturated and trans fats) or high in sodium
can increase your risk of certain chronic diseases.
• 5% or less of the daily value (DV) of a portion of a nutrient is low
• 20% or less of the daily value (DV) of a portion of a nutrient is high
5. Carbohydrates
Observe at the total amount, this includes fiber, complex carbohydrates and sugar.
• Increase dietary fiber: focus on options providing 3g or more
• Limit added sugar: focus on options with 5g or less
6. Protein
Essential component in the diet. Select lean cuts and consume fish
at least 2 times per week.
7. Vitamins & Minerals
Getting the most of these nutrients can help improve your health.
Importance of good nutrition
for people with diabetes
An important factor in the management of diabetes is controlling the amount of carbohydrates and added sugar ingested in food.
In that sense, the diet is a key point for the comprehensive management of diabetes. Good nutrition can help you achieve optimal levels of the nutrients your body needs.
Plate method for people with diabetes.
The plate method is the easiest way to prepare healthy meals that help manage blood sugar. With this method, you can create balanced dishes, without the need to count, calculate, weigh or measure.
To start, you need a plate that is not too big. A reasonable size is 9 inches.
dividing it in three sections

Vegetable Salads
Fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables like carrot, cauliflower, eggplant, peppers, lettuce and broccoli.
Proteins
Fill a quarter of your plate with food rich in lean proteins like fish, chicken, beef, soy products, plant-based meat substitutes.
Carbohydrates
Limit a quarter of your plate with carbohydrates such as whole grain products (bread, cereal, rice & pasta), starchy vegetables (potato, pumpkin, plantain) and beans and legumes.

Water or low-calorie beverages
Options include unsweetened tea, carbonated water with no sugar added.
Meal Plan Calorie Options
Breakfast
- 2 Scramble Eggs
- toast of Whole Grain Bread
- ¼ cup of Strawberries
- oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- 3 oz of baked Pork Chop
- 1 medium baked Sweet Potato
- 1 cup of shredded Cabbage & Carrot salad
- 1 tsp of Olive Oil & Balsamic Vinegar
Dinner
- 3 oz of grilled Salmon
- 1 cup of Whole Wheat Pasta in red sauce
- 1 cup of steamed Cauliflower
Breakfast
- 1/4 cup of Granola
- 3/4 cup of Blueberries
- 1/2 Banana
- 6 oz of Greek Yogurt
- 4 oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- Wrap with:
- 3 oz of ground Turkey
- 1 of 12″ Flour Tortilla
- 1 oz of Swiss Cheese
- 1 cup of Lettuce & Tomato
Dinner
- 3 oz of Grouper in Tamarind Sauce
- 1 cup of mashed Potatoes
- 1 cup of roasted Asparagus
- 1 tsp of Avocado Oil
Breakfast
- 3 Scramble Eggs
- 1 toast of Whole Grain Bread
- 1 ¼ cup of Strawberries
- 4 oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- 3 oz of baked Pork Chop
- 1 medium baked Sweet Potato
- 1 cup of shredded Cabbage & Carrot salad
- 1 tsp of Olive Oil & Balsamic Vinegar
Dinner
- 3 oz of grilled Salmon
- 1 cup of Whole Wheat Pasta in red sauce
- 1 cup of steamed Cauliflower
Breakfast
- 1/4 cup of Granola
- 3/4 cup of Blueberries
- 1/2 Banana
- 1 tbsp of chia seeds
- 6 oz of Greek Yogurt
- 4 oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- Wrap with:
- 3 oz of ground Turkey
- 1 of 12″ Flour Tortilla
- 1 oz of Swiss Cheese
- 1 cup of Lettuce & Tomato
Dinner
- 3 oz of Grouper in Tamarind Sauce
- 1 cup of mashed Potatoes
- 1 cup of roasted Asparagus
- 1 tsp of Avocado Oil
Snacks
- 1 Tangerine
- 1 stick of Mozzarella Cheese
- 14 red Grapes
- 1 Glucerna shake
- 1 Glucerna Hunger Smart Shake
- 3/4 cup of Pineapple
Breakfast
- 3 Scramble Eggs
- 2 toast of Whole Grain Bread
- 1 ¼ cup of Strawberries
- 4 oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- 3 oz of baked Pork Chop
- 1 1/3 large baked Sweet Potato
- 1 cup of shredded Cabbage & Carrot salad
- 1 tsp of Olive Oil & Balsamic Vinegar (if desired)
Dinner
- 3 oz of grilled Salmon
- 1 cup of Whole Wheat Pasta in red sauce
- 1 cup of steamed Cauliflower
Breakfast
- 1/4 cup of Granola
- 3/4 cup of Blueberries
- 1/2 Banana
- 1 tbsp of chia seeds
- 6 oz of Greek Yogurt
- 4 oz of Low-Fat Milk (optional add coffee)
Lunch
- Wrap with:
- 4 oz of ground Turkey
- 1 of 12″ Flour Tortilla
- 1 oz of Swiss Cheese
- 1 cup of Lettuce & Tomato
Dinner
- 4 oz of Grouper in Tamarind Sauce
- 1 1/2 cup of mashed Potatoes
- 1 cup of roasted Asparagus
- 1 tsp of Avocado Oil
Snacks
- 1 Tangerine
- 3 cups of Light Popcorn
- 1 stick of Mozzarella Cheese
- 14 red Grapes
- 1 Glucerna shake
- 1 Glucerna Hunger Smart Shake
- 1 1/2 cup of Pineapple
